Common Dog Group Classifications:
- Sporting Group – Energetic and alert dogs bred for hunting and retrieving, such as Retrievers and Spaniels. They need lots of exercise.
- Hound Group – Known for their powerful scenting or sighting abilities. Includes breeds like Beagles and Greyhounds.
- Working Group – Strong, intelligent dogs bred for tasks like guarding or pulling sleds, e.g., Boxers and Huskies.
- Terrier Group – Feisty and energetic, bred to hunt and dig out vermin. Examples: Bull Terriers, Scottish Terriers.
- Toy Group – Small, companion-focused breeds like Chihuahuas and Pomeranians. They’re affectionate and suited for indoor living.
- Non-Sporting Group – Diverse group with varied sizes and purposes, like Bulldogs and Dalmatians.
- Herding Group – Intelligent and driven, originally bred to herd livestock. Includes Border Collies and German Shepherds.
- Miscellaneous/Other – Breeds working toward full recognition. Their characteristics vary widely.
Detailed Description of the Major Dog Breed Group Characteristics
1. Sporting Group
Purpose: Bred to assist hunters in the field by locating, flushing, and retrieving game.
Traits:
- Energetic, alert, and intelligent.
- Excellent companions for active individuals or families.
- Love water and retrieving (especially retrievers and spaniels).
- Require regular exercise and mental stimulation. Examples: Labrador Retriever, Golden Retriever, Cocker Spaniel, Weimaraner.
2. Hound Group
Purpose: Developed for hunting by scent (scenthounds) or sight (sighthounds).
Traits:
- Strong prey drive and hunting instincts.
- Scenthounds (e.g., Bloodhounds) have incredible olfactory abilities.
- Sighthounds (e.g., Greyhounds) are fast, lean, and graceful.
- Often independent and may be less responsive to training. Examples: Beagle, Basset Hound, Afghan Hound, Dachshund.
3. Working Group
Purpose: Bred for jobs like guarding property, pulling sleds, or performing rescues.
Traits:
- Intelligent, powerful, and alert.
- Naturally protective, often used in police/military roles.
- Need confident, experienced handlers.
- Require consistent training and exercise. Examples: Boxer, Rottweiler, Siberian Husky, Great Dane.
4. Terrier Group
Purpose: Originally bred to hunt and kill vermin and protect homes and barns.
Traits:
- Feisty, energetic, and bold.
- Tenacious and often fearless.
- Can be stubborn and independent.
- Require early socialization and training. Examples: West Highland White Terrier, Scottish Terrier, Bull Terrier, Airedale Terrier.
5. Toy Group
Purpose: Bred primarily as companions and lapdogs.
Traits:
- Small in size, but often bold in personality.
- Loyal, affectionate, and thrive on attention.
- Ideal for apartment living.
- Require socialization to prevent excessive barking or possessiveness. Examples: Pomeranian, Cavalier King Charles Spaniel, Chihuahua, Pekingese.
6. Non-Sporting Group
Purpose: A diverse group of breeds that don’t fit neatly into other categories.
Traits:
- Wide variety in size, coat, temperament, and appearance.
- Many were bred for companionship, some for specific tasks (like guarding or circus performance).
- Adaptability depends on the breed. Examples: Bulldog, Dalmatian, Poodle, Boston Terrier.
7. Herding Group
Purpose: Bred to control and move livestock.
Traits:
- Highly intelligent and responsive to training.
- Strong herding instincts—may try to herd children or other pets.
- Energetic and need regular mental and physical stimulation.
- Loyal and often form strong bonds with their people. Examples: Border Collie, Australian Shepherd, German Shepherd, Shetland Sheepdog.
8. Miscellaneous Group / Foundation Stock Service (FSS)
Purpose: Breeds that are not yet fully recognized by the AKC but are in development.
Traits:
- Vary widely based on the breed’s original purpose.
- May be newer or rare breeds gaining popularity and recognition. Examples: Not a fixed group; examples change over time (e.g., Russian Toy, Mudi).
10 common dog breeds from each AKC dog group
🐾1. Sporting Group
🐾 2. Hound Group
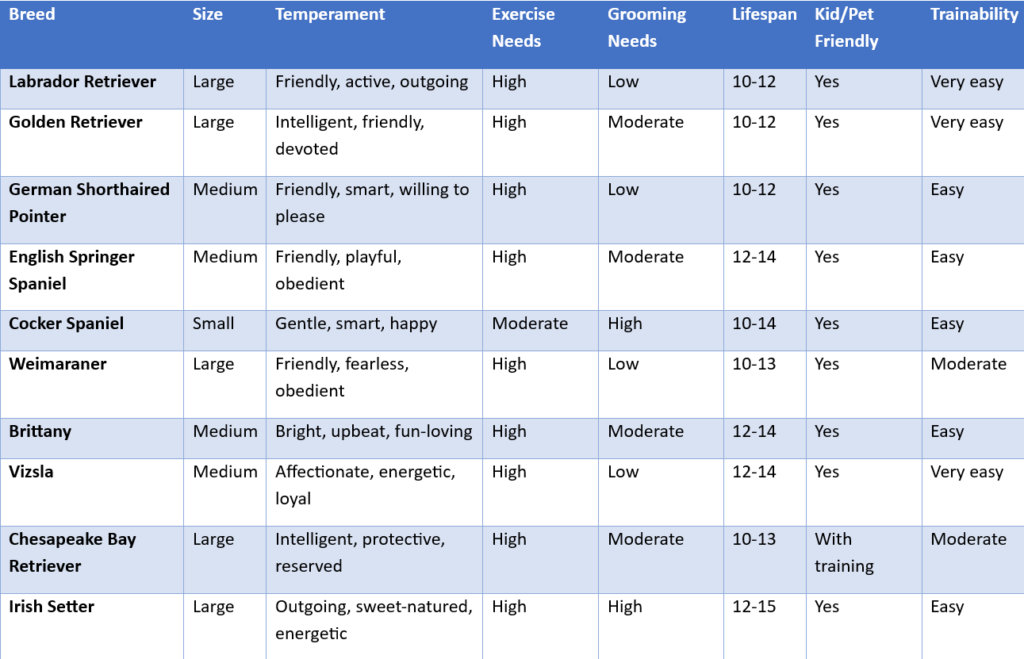
- Labrador Retriever
- Golden Retriever
- English Springer Spaniel
- Cocker Spaniel
- Weimaraner
- German Shorthaired Pointer
- Vizsla
- Chesapeake Bay Retriever
- Irish Setter
- Brittany
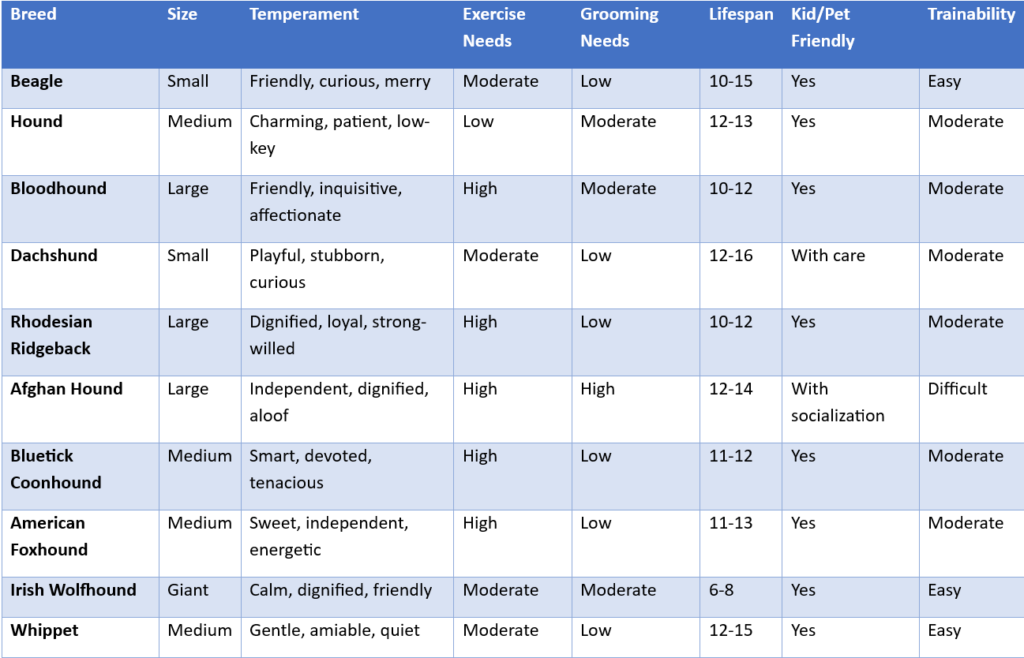
- Beagle
- Dachshund
- Basset Hound
- Bloodhound
- Greyhound
- Afghan Hound
- Rhodesian Ridgeback
- Whippet
- Irish Wolfhound
- Basenji
🐾 3. Working Group
🐾 4. Terrier Group
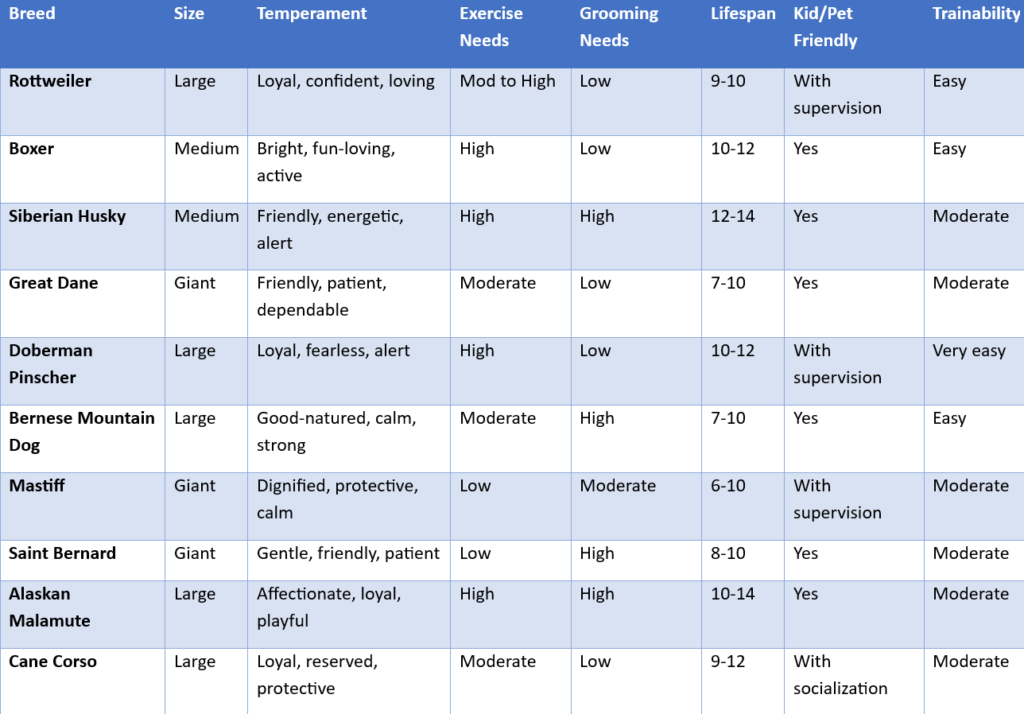
- Boxer
- Rottweiler
- Siberian Husky
- Great Dane
- Doberman Pinscher
- Bernese Mountain Dog
- Mastiff
- Saint Bernard
- Alaskan Malamute
- Akita
- West Highland White Terrier
- Bull Terrier
- Scottish Terrier
- Jack Russell Terrier (Parson Russell)
- Airedale Terrier
- Miniature Schnauzer
- Cairn Terrier
- Border Terrier
- Wire Fox Terrier
- American Staffordshire Terrier
🐾 5. Toy Group
🐾 6. Non-Sporting Group
- Pomeranian
- Chihuahua
- Maltese
- Cavalier King Charles Spaniel
- Yorkshire Terrier
- Toy Poodle
- Papillon
- Shih Tzu
- Italian Greyhound
- Pekingese
- Bulldog
- Poodle (Standard & Miniature)
- Dalmatian
- Boston Terrier
- Bichon Frise
- Lhasa Apso
- Shiba Inu
- Chinese Shar-Pei
- Chow Chow
- American Eskimo Dog
🐾 7. Herding Group
🐾 8. Miscellaneous / FSS Group
- Border Collie
- German Shepherd Dog
- Australian Shepherd
- Shetland Sheepdog
- Collie
- Belgian Malinois
- Pembroke Welsh Corgi
- Cardigan Welsh Corgi
- Old English Sheepdog
- Australian Cattle Dog
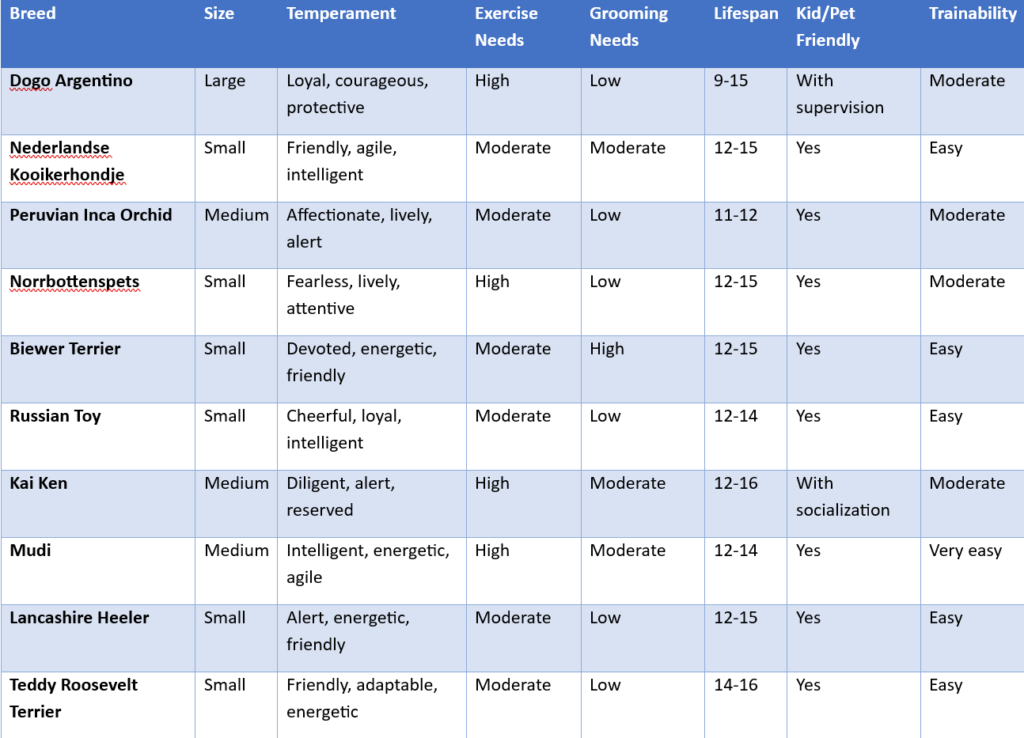
- Mudi
- Russian Toy
- Lancashire Heeler
- Bracco Italiano
- Barbet
- Azawakh
- Biewer Terrier
- Peruvian Inca Orchid
- Norrbottenspets
- Kai Ken
Breed Characteristics in each grOUP
Sporting group
hound group
working group
Terrier group
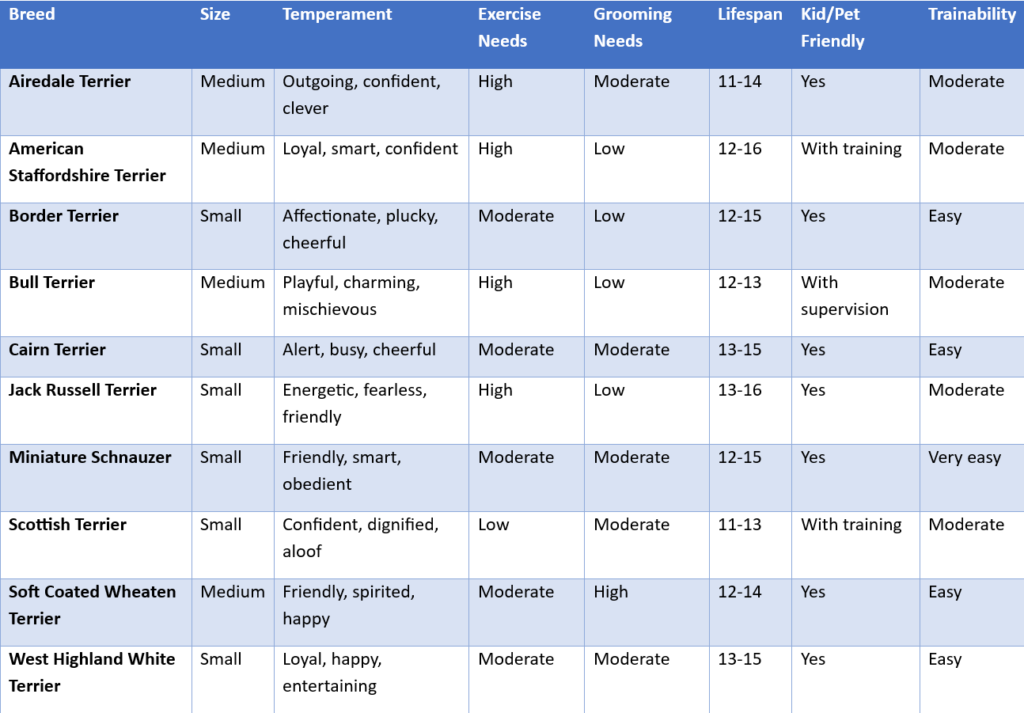
toy group
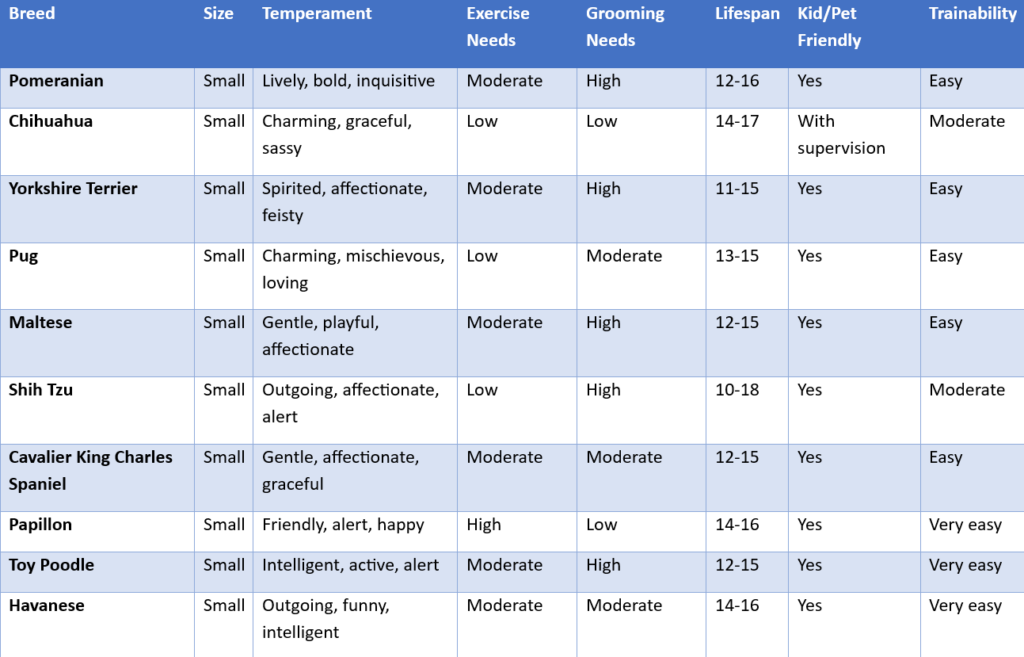
non-sporting group
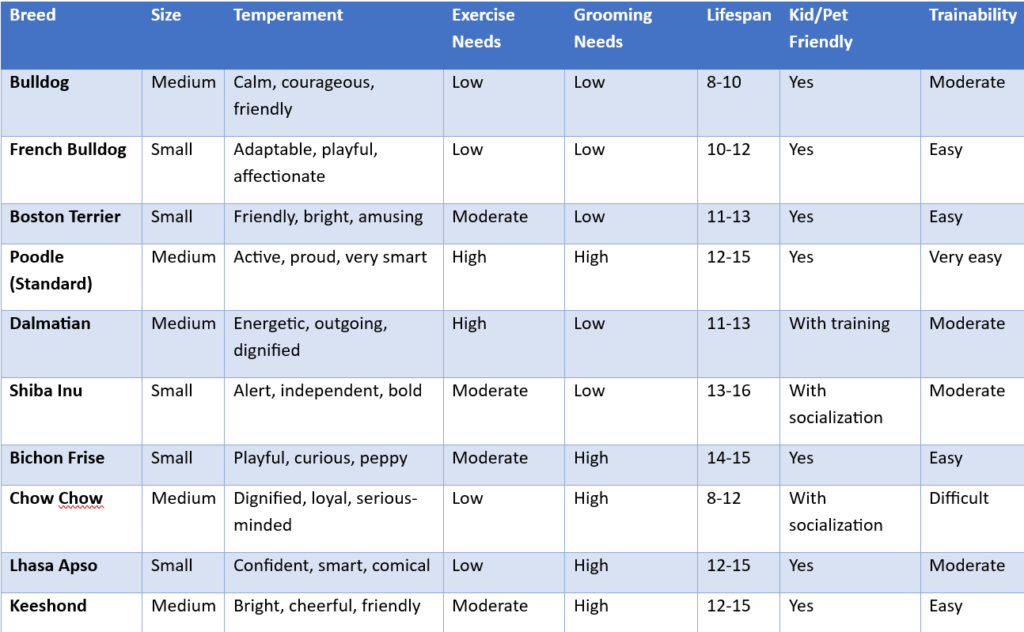
herding group
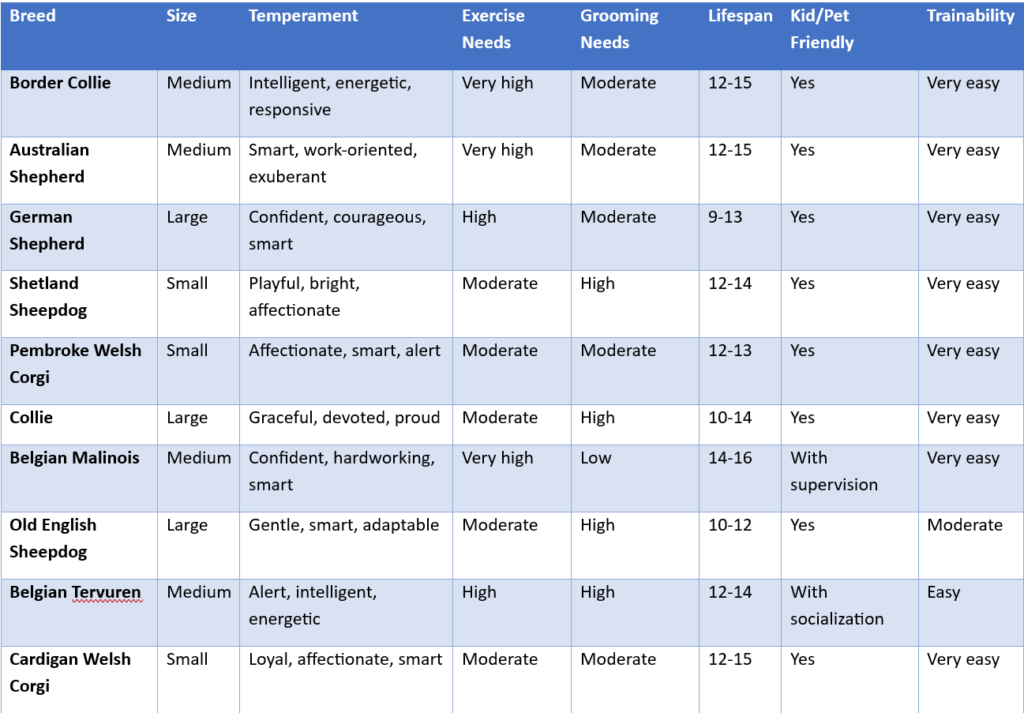
miscellaneous/other group